Content
- Discount Rates, Default Risk And Asset Pricing In A Regime Change Model
- Stock Price Fluctuations
- 4 Spillovers From Health Human Capital Beyond The Individual And Family
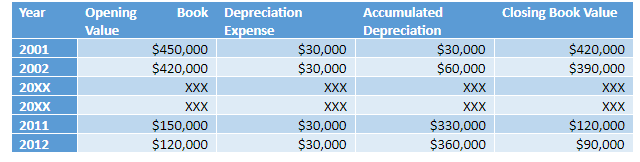
- Explaining Capital Stock In Context
- Why Is Capital Stock Important?
- What Are The Advantages Of Capital Stock?
- What Are The Components Of Paid
- How Does A Share Premium Account Appear On The Balance Sheet?
- Capital Stock Real Capital, Capital Goods
- Selling
Capital Stockmeans, with respect to any Person, any capital stock , shares, interests, participations or other ownership interests of such Person and any rights , warrants or options to purchase any thereof. Financing a company through the sale of stock in a company is known as equity financing. Alternatively, debt financing can be done to avoid giving up shares of ownership of the company. Unofficial financing known as trade financing usually provides the major part of a company’s working capital (day-to-day operational needs). Although ownership of 50% of shares does result in 50% ownership of a company, it does not give the shareholder the right to use a company’s building, equipment, materials, or other property. This is because the company is considered a legal person, thus it owns all its assets itself.
- The choice of mechanism for clearing the budget is often an important part of the simulations.
- Convertible preferred stock is preferred stock that includes an option for the holder to convert the preferred shares into a fixed number of common shares, usually any time after a predetermined date.
- Here, supervoting shares may have the votes to overwhelm the voting power of other shares.
- Metrics are crucial for business planning, making informed decisions, defining strategic targets, and measuring performance.
- A recent study shows that customer satisfaction, as measured by the American Customer Satisfaction Index , is significantly correlated to the market value of a stock.
It can be altered by making changes to its legal charter after following prescribed procedures. Eventually, sellers attracted to the high selling price enter the market and/or buyers leave, achieving equilibrium between buyers and sellers. Eventually buyers enter and/or sellers leave, again achieving equilibrium. As with buying a stock, there is a transaction fee for the broker’s efforts in arranging the transfer of stock from a seller to a buyer. This fee can be high or low depending on which type of brokerage, full service or discount, handles the transaction. Generally, the investor wants to buy low and sell high, if not in that order ; although a number of reasons may induce an investor to sell at a loss, e.g., to avoid further loss. The largest shareholders are often mutual funds, and, especially, passively managed exchange-traded funds.
Discount Rates, Default Risk And Asset Pricing In A Regime Change Model
If the allocation price of shares is greater than the par value, as in a rights issue, the shares are said to be sold at a premium (variously called share premium, additional paid-in capital or paid-in capital in excess of par). Commonly, the share capital is the total of the nominal share capital and the premium share capital. Most jurisdictions do not allow a company to issue shares below par value, but if permitted they are said to be issued at a discount or part-paid. Many “par value states” mandate that corporations report excesses over the par or face amount of shares sold in a separate account. If a corporation sold 1 million shares of common stock to investors for $10 a share with each share having a par value of one penny, the corporation would report a $10 million cash asset. In the shareholders’ equity section, the corporation would report $10,000 in the “common stock” account — 1 million shares multiplied by $0.01, and $9,990,000 in the “capital surplus” account. In “no par value states,” the corporation would report the entire $10 million in the common stock account in the shareholders’ equity section.
Reliance on foreign resources also tends to bring about real exchange rate appreciation, slower export growth and more rapid growth in imports and production of non-tradables. The strength of these effects depends on the growth impact of the expansion in government spending as well as on whether the new spending has high or low import shares. The alternative of raising direct taxes tends to be less favorable to growth in GDP and private final demand than reliance on foreign resources.
Yet, their total income at this date, I0, may include other sources of income as well. Equation (4.48) concludes the series of equations that summarize the government budget, see also Equations (4.40), (4.41) and (4.44). The choice of mechanism for clearing the budget is often an important part of the simulations. As noted above, in this mathematical statement it is assumed that changes in the variable DTINSt, see Equation (4.34) and adjust direct tax payments sufficiently to clear the budget. The other terms in the expressions for government receipts and outlays are exogenous or determined via other mechanisms. Under alternative government closures, DTINSt is exogenous while some other variable is endogenous, clearing the government budget, e.g. government bond sales or government borrowing from the rest of the world .
Capital stock can be issued by a company to raise capital to grow its business. Issued shares can be bought by investors—who seek price appreciation and dividends—or exchanged for assets, such as equipment needed for operations. It refers to plant, equipment and other assets that facilitate production.
Stock Price Fluctuations
It is a process that only goes on between shareholders and has no impact on accounting or bookkeeping unless the company actually buys them back . When a share is issued, it is identified by a share certificate or stock certificate that can be traded by the shareholder. A corporate kit is a collection of a company’s corporate charter, minutes from shareholder meetings, benefit plan documents, the stock register, and the stock certificate book. Additional paid-in capital is the excess amount paid by an investor above the par value price of a stock during an initial public offering . Capital Stockmeans, for any entity, any and all shares, interests, rights to purchase, warrants, options, participations or other equivalents of or interests in stock issued by that entity.
Stock price may be influenced by analysts’ business forecast for the company and outlooks for the company’s general market segment. Many large non-U.S companies choose to list on a U.S. exchange as well as an exchange in their home country in order to broaden their investor base. These companies must maintain a block of shares at a bank in the US, typically a certain percentage of their capital. On this basis, the holding bank establishes American depositary shares and issues an American depositary receipt for each share a trader acquires. Likewise, many large U.S. companies list their shares at foreign exchanges to raise capital abroad.
4 Spillovers From Health Human Capital Beyond The Individual And Family
When companies do this, it is usually so that they can raise more capital. The amount of capital stock is the maximum amount of shares that a company can ever have outstanding. Capital Stockmeans any and all shares, interests, participations, rights or other equivalents of corporate stock. Adam Smith’s Wealth of Nations2 receives credit for imparting an economic meaning to “capital.” By Smith’s definition, capital is stock, while profit refers to realizing the revenue from improvements made to that stock. Smith also viewed capital improvement the preferred objective for the economic and system. Note, however, that Smith called his ideal economic system “natural liberty,” although others later named it “Capitalism.”
It appears as the owner’s or shareholders’ equity on the corporate balance sheet’s liability side. In finance, stock consists of all of the shares into which ownership of a corporation or company is divided. (Especially in American English, the word “stocks” is also used to refer to shares.) A single share of the stock means fractional ownership of the corporation in proportion to the total number of shares.
Explaining Capital Stock In Context
Outstanding shares are shares that have been issued to investors and are not owned by the company. To figure out your company’s outstanding shares, simply subtract the number of treasury shares from the total number of issued shares. Firms can issue some of the capital stock over time or buy back shares that are currently owned by shareholders. Previously outstanding shares that are bought back by the company are known as Treasury shares. The amount that a company receives from issuing capital stock is considered to be capital contributions from investors and is reported as paid-in capital and additional paid-in capital in the stockholder’s equity section of the balance sheet. Issued SharesShares Issued refers to the number of shares distributed by a company to its shareholders, who range from the general public and insiders to institutional investors.
- Finding out the par value of a common stock or per share value, in other words, is easy, as this information is readily available in the stock certificates.
- A keen investor with access to information about such discrepancies may invest in expectation of their eventual convergence, known as arbitrage trading.
- Accordingly, capital guidelines discourage overreliance on nonvoting equity elements in Tier 1 capital.
- Reliance on foreign resources also tends to bring about real exchange rate appreciation, slower export growth and more rapid growth in imports and production of non-tradables.
- The desire of stockholders to trade their shares has led to the establishment of stock exchanges, organizations which provide marketplaces for trading shares and other derivatives and financial products.
- Different classes of shares include ordinary shares, preference shares, growth shares and deferred shares.
- Most jurisdictions do not allow a company to issue shares below par value, but if permitted they are said to be issued at a discount or part-paid.
So as long as the shareholders agree that the management are performing poorly they can select a new board of directors which can then hire a new management team. Board candidates are usually nominated by insiders or by the board of the directors themselves, and a considerable amount of stock is held or voted by insiders. Different classes of shares include ordinary shares, preference shares, growth shares and deferred shares. Shares will be a separate class if the rights attached to them differ from the rights attached to other shares in the capital of the company. The legal aspects of share capital are mostly dealt with in a jurisdiction’s corporate law system. An example of such an issue is that when a company allocates new shares, it must do so without inequitably diluting its existing shareholders. In practice, the concept of “par value” has very little meaning, since shares usually represent a residual claim; they do not endow their owners with a claim toward any fixed sum of money.
Why Is Capital Stock Important?
New equity issue may have specific legal clauses attached that differentiate them from previous issues of the issuer. Some shares of common stock may be issued without the typical voting rights, for instance, or some shares may have special rights unique to them and issued only to certain parties. Often, new issues that have not been registered with a securities governing body may be restricted from resale for certain periods of time. Legal capital is a concept used in UK company law, EU company law, and various other corporate law jurisdictions to refer to the sum of assets contributed to a company by shareholders when they are issued shares. The law often requires that this capital is maintained, and that dividends are not paid when a company is not showing a profit above the level of historically recorded legal capital. The prices of new capital stocks depend on their composition and market prices, Equation (4.47). The resulting fixed government investment value is financed by some combination of government savings , sales of government bonds (i.e. new interest-bearing borrowing), borrowing via the monetary system, foreign borrowing and foreign capital grants , Equation (4.48).
- It refers to plant, equipment and other assets that facilitate production.
- A stock derivative is any financial instrument for which the underlying asset is the price of an equity.
- A capital instrument deemed not permanent or that has preference with regard to liquidation or payment of dividends is not considered common stock, regardless of what investors call the instrument.
- However, in a few unusual cases, some courts have been willing to imply such a duty between shareholders.
- Holders of preferred stock have right on fixed dividends and take precedence over common stockholders in case of bankruptcy.
- A company issued 5,000 shares at $6 per share, having a par value of $5 each.
Treasury SharesTreasury Stock is a stock repurchased by the issuance Company from its current shareholders that remains non-retired. Moreover, it is not considered while calculating the Company’s Earnings Per Share or dividends. However, in a few unusual cases, some courts have been willing to imply such a duty between shareholders.
In the common case of a publicly traded corporation, where there may be thousands of shareholders, it is impractical to have all of them making the daily decisions required to run a company. Thus, the shareholders will use their shares as votes in the election of members of the board of directors of the company. By selling shares they can sell part or all of the company to many part-owners. The purchase of one share entitles the owner of that share to literally share in the ownership of the company, a fraction of the decision-making power, and potentially a fraction of the profits, which the company may issue as dividends. The innovation of joint ownership made a great deal of Europe’s economic growth possible following the Middle Ages.
To bypass the problem of double counting and likely overreporting in the official investment statistics, I had to use a bottom-up approach to reconstruct the investment flow by industry. The core variable was OVFA in official industrial statistics covering fixed assets already engaged in production. Once a stock is repurchased the company can either cancel it, reissue it, or hold onto it. An investor can buy stock from a corporation and in return they hope to receive benefits known as dividends. Capital stock is not necessarily equal to the number of shares that are currently outstanding. If a company wants to change this number, they have to change it on their charter.
What Are The Advantages Of Capital Stock?
Once the rate of requests has dropped below the threshold for 10 minutes, the user may resume accessing content on SEC.gov. This SEC practice is designed to limit excessive automated searches on SEC.gov and is not intended or expected to impact individuals browsing the SEC.gov website. The oldest share in the world, issued by the Dutch East India Company (Vereenigde Oost-Indische Compagnie or VOC), 1606. Stock futures are contracts where the buyer is long, i.e., takes on the obligation to buy on the contract maturity date, and the seller is short, i.e., takes on the obligation to sell.

Companies can also buy back stock, which often lets investors recoup the initial investment plus capital gains from subsequent rises in stock price. Stock options issued by many companies as part of employee compensation do not represent ownership, but represent the right to buy ownership at a future time at a specified price. This would represent a windfall to the employees if the option is exercised when the market price is higher than the promised price, since if they immediately sold the stock they would keep the difference . Capital stock is stock that is authorized and issued according to a corporation’s charter. It includes common stock and preferred stock, and denotes the capital contributions the corporation receives from its initial investors. The method of reporting the value of capital stock in the shareholders’ equity section of a balance sheet depends on whether the stock is issued with or without a stated value — commonly called par value.
We compare magnitudes, trends, and dynamics based on different measures of human capital, including traditional education-based human capital indexes and the Jorgenson-Fraumeni (J-F) lifetime income measure. Because of the drastic disparities in economic development within Mainland China, we compare two of its most advanced cities, Beijing and Shanghai, with Hong Kong and Taiwan. We also discuss how human capital growth interacts with the impact of population aging on population dividends.
What Are The Components Of Paid
The technique of pooling capital to finance the building of ships, for example, made the Netherlands a maritime superpower. Before the adoption of the joint-stock corporation, an expensive venture such as the building of a merchant ship could be undertaken only by governments or by very wealthy individuals or families. The Dutch East India Company became the first multinational corporation and the first megacorporation. Between 1602 and 1796 it traded 2.5 million tons of cargo with Asia on 4,785 ships and sent a million Europeans to work in Asia, surpassing all other rivals.
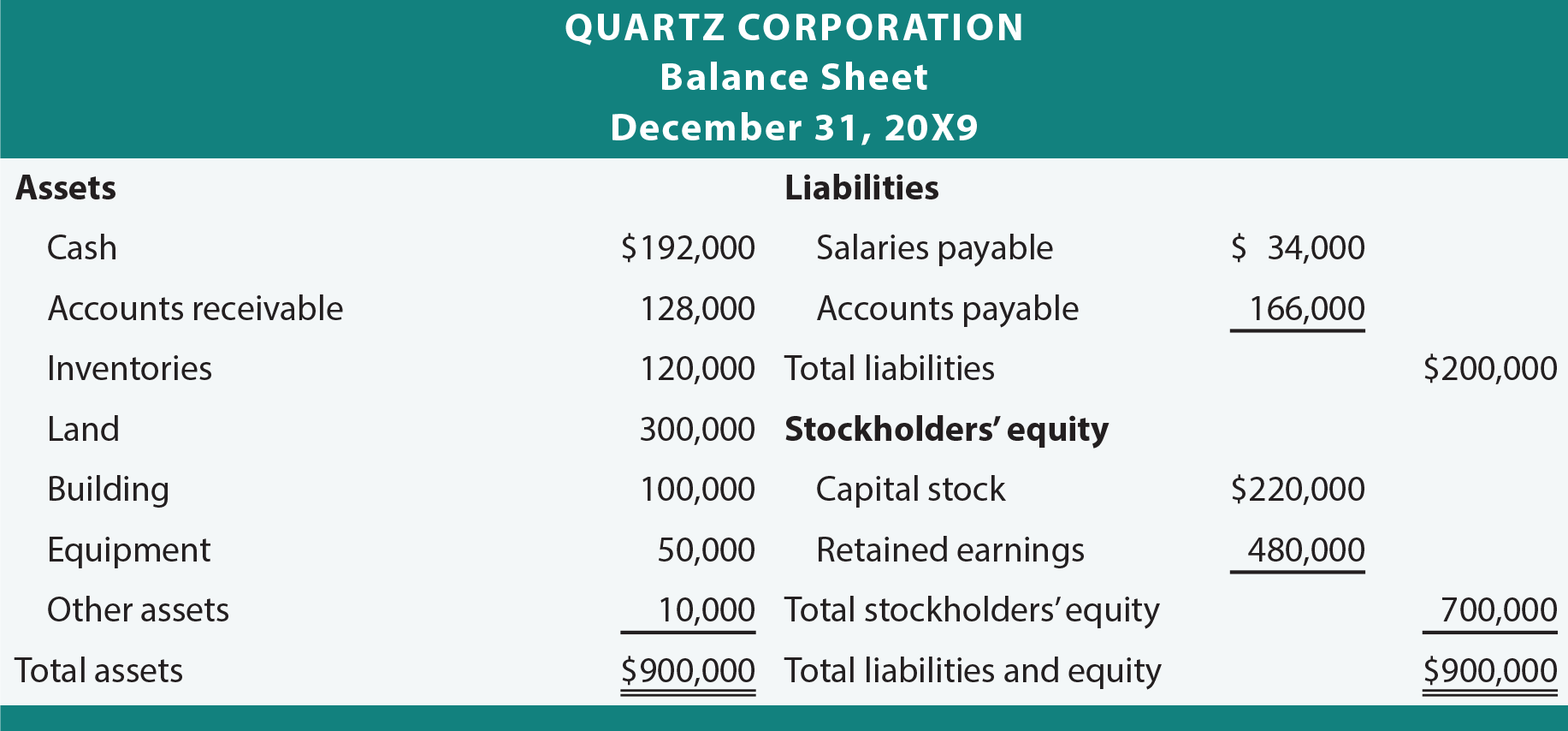
In accounting, ledger account is one part of the equity section on a balance sheet.’ Only corporations can sell capital stock to investors. Stock can be bought and sold privately or on stock exchanges, and such transactions are typically heavily regulated by governments to prevent fraud, protect investors, and benefit the larger economy. The stocks are deposited with the depositories in the electronic format also known as Demat account. As new shares are issued by a company, the ownership and rights of existing shareholders are diluted in return for cash to sustain or grow the business.
Learn the best ways to calculate, report, and explain NPV, ROI, IRR, Working Capital, Gross Margin, EPS, and 150+ more cash flow metrics and business ratios. The Balance Sheet summarizes the value of the firm’s Assets, Liabilities, and Equities at one point in time. Companies normally publish the Balance Sheet and other financial statements just after the close of a financial quarter or year. The approval of stockholders is required to make major decisions in the company. It shows the trust of the investors in the company and thus increases its credibility. If a user or application submits more than 10 requests per second, further requests from the IP address may be limited for a brief period.
- Capital stock refers to the shares of ownership that have been issued by a corporation.
- A business that has a relatively small amount of capital stock is said to be thinly capitalized, and probably relies upon a significant amount of debt to fund its operations.
- However, this should not mean that a corporation with more debt on its balance sheet would not be a safe bet to invest in.
- States wanted corporations to keep a reserve of funds available for creditors in the event of a bankruptcy.
- As the name suggests, retained earnings are the earnings of the corporation that are retained for either reinvestment in its core business or for repayment of debt.
- To bypass the problem of double counting and likely overreporting in the official investment statistics, I had to use a bottom-up approach to reconstruct the investment flow by industry.
Corporations record capital stock in the equity section on their balance sheets. The amount of capital stock issuable by a company can be changed, but the process requires amending the corporate charter, usually involving difficult, expensive shareholder voting. In order to better understand the concept of capital stock, it is important to have a basic idea of common stock and preferred stock of a company and the difference between the two.
The underlying security may be a stock index or an individual firm’s stock, e.g. single-stock futures. A business may declare different types of shares, each having distinctive ownership rules, privileges, or share values. A stock certificate is a legal document that specifies the number of shares owned by the shareholder, and other specifics of the shares, such as the par value, if any, or the class of the shares.
If more investors are selling a stock and there aren’t enough buyers, the price will go down. There are various methods of buying and financing stocks, the most common being through a stockbroker. Brokerage firms, whether they are a full-service or discount broker, arrange the transfer of stock from a seller to a buyer. Most trades are actually done through brokers listed with a stock exchange. Corporations may, however, issue different classes of shares, which may have different voting rights. Owning the majority of the shares allows other shareholders to be out-voted – effective control rests with the majority shareholder . In this way the original owners of the company often still have control of the company.

After the transaction has been made, the seller is then entitled to all of the money. Importantly, on selling the stock, in jurisdictions that have them, capital gains taxes will have to be paid on the additional proceeds, if any, that are in excess of the cost basis. A stock derivative is any financial instrument for which the underlying asset is the price of an equity.
In economics, the term capital stock is approximately interchangeable with the terms capital goods, real capital, or capital assets. By any of these names, capital stock items are already-produced, durable goods or any nonfinancial asset that works for the production of goods or services. When companies raise capital by offering stock on more than one exchange, the potential exists for discrepancies in the valuation of shares on different exchanges. A keen investor with access to information about such discrepancies may invest in expectation of their eventual convergence, known as arbitrage trading. Electronic trading has resulted in extensive price transparency (efficient-market hypothesis) and these discrepancies, if they exist, are short-lived and quickly equilibrated.
For example, in California, USA, majority shareholders of closely held corporations have a duty not to destroy the value of the shares held by minority shareholders. The earliest recognized joint-stock company in modern times was the English East India Company, one of the most notorious joint-stock companies.
Estimates of the individual components on the right-hand side provide an estimate of the user cost, which is, itself, assumed to equal the value of the marginal product of capital in competitive equilibrium. A stock register is a list of all shareholder’s contact information, how many shares they own, and the identifying number of each share that is owned. Treasury stock is previously outstanding stock bought back from stockholders by the issuing company. Shares are a unit of ownership of a company that may be purchased by an investor. Khadija Khartit is a strategy, investment, and funding expert, and an educator of fintech and strategic finance in top universities. She has been an investor, entrepreneur, and advisor for more than 25 years.
If at least one share is owned, most companies will allow the purchase of shares directly from the company through their investor relations departments. However, the initial share of stock in the company will have to be obtained through a regular stock broker. Another way to buy stock in companies is through Direct Public Offerings which are usually sold by the company capital stock itself. A direct public offering is an initial public offering in which the stock is purchased directly from the company, usually without the aid of brokers. Small companies that do not qualify and cannot meet the listing requirements of the major exchanges may be traded over-the-counter by an off-exchange mechanism in which trading occurs directly between parties.
The term Capital appears in quite a few different terms, with different meanings in business finance, investing, budgeting—and the field of Economics. However, all of these meanings have in common a reference to substantial resources for producing goods and services.
Selling
It is filed with the state government of whatever state the company incorporates in. It details things like a company’s location, whether it will be a profit or nonprofit, its board composition, and its ownership structure. This also is where a company will state the number of authorized stock they intend to use. Paid-in capital is the capital paid in by investors during common or preferred stock issuances. If a company obtains authorization to raise $5 million and its stock has a par value of $1, it may issue and sell up to 5 million shares of stock. The difference between the par value and the sale price of the stock is logged under shareholders’ equity as additional paid-in capital.
What are the basic rights associated with a share of capital stock if there is only one class of stock outstanding?
The basic rights of each stockholder (unless otherwise restricted) are to share proportionately: (1) in profits, (2) in management (the right to vote for directors), (3) in corporate assets upon liquidation, and (4) in any new issues of stock of the same class (preemptive right). 2.
Financial capital refers to the cash in hand and obligations, if any, left after the production process is over. Human capital would essentially include the value of acquired skills and talent. Social capital would mean the value of relationships built during the process. Economists used this term to get a pulse of the output level an economy has the capacity to produce. Free AccessFinancial Metrics ProKnow for certain you are using the right metrics in the right way.
The Dutch stock market of the 17th century included the use of stock futures, stock options, short selling, the use of credit to purchase shares, a speculative bubble that crashed in 1695, and a change in fashion that unfolded and reverted in time with the market. Edward Stringham also noted bookkeeping that the uses of practices such as short selling continued to occur during this time despite the government passing laws against it. This is unusual because it shows individual parties fulfilling contracts that were not legally enforceable and where the parties involved could incur a loss.
In general, the shares of a company may be transferred from shareholders to other parties by sale or other mechanisms, unless prohibited. Most jurisdictions have established laws and regulations governing such transfers, particularly if the issuer is a publicly traded entity. Shareholders are one type of stakeholders, who may include anyone who has a direct or indirect equity interest in the business entity or someone with a non-equity interest in a non-profit organization. Thus it might be common to call volunteer contributors to an association stakeholders, even though they are not shareholders. These conditions are implied by our assumption that firms observe the state of nature prior to their decision about borrowing capital and hiring labor.
Author: Craig W. Smalley, E.A.